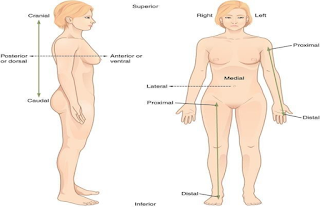
Radiographic positioning terminology
Radiographic positioning terminology is used routinely to describe the position of the patient for taking various radiographs. Standard nomenclature is employed concerning the anatomic position.
Terminology
Basic terms of relations
v
Anterior is towards the
front of the body (Latin: before)
v
Posterior is towards the
back of the body (Latin: after)
v
Superior is towards the
top of the body (Latin: above)
v
Inferior is towards the
bottom of the body (Latin: below)
v
Medial is towards the
midline (Latin: middle)
Compared with the median which is in the midline rather than towards the midline?
v
Lateral is away from the
midline (Latin: side)
v
Proximal is towards the
centre of the body (Latin: near)
v
Distal is away from the
centre of the body (Latin: far)
v
Superficial is towards the
surface of the body
v
Deep is away from the
surface of the body
v
Ipsilateral is on the same
side of the body
v
Contralateral is on the
opposite side of the body
Movement
v
Flexion: decrease in the
angle of the joint
v
Extension: increase in the
angle of the joint
v
Abduction: Movement of a limb
away from the midline
v
Adduction: Movement of a limb
towards the midline
v Pronation: movement of hand and forearm to bring the palm facing posteriorly
v Supination: movement of hand and forearm to bring the palm facing
anteriorly
v Opposition: thumb brought to oppose
another digit
v
Reposition: thumb
repositioned back to the anatomic position
v
Elevation: movement of the
scapular superiorly
v
Depression: movement of the
scapular inferiorly
v
Eversion: Movement of the
sole away from the median plane
v
Inversion: Movement of the
sole towards the median plane
v
Protrusion: movement of the
mandible, lips, or tongue anteriorly
v
Retraction: movement of the
mandible, lips, or tongue posteriorly
Body positions
v
Erect: either standing
or sitting
v
Decubitus: lying down
v
Supine: lying on back
v
Prone: lying face-do
v
Lateral decubitus: lying on one side
v
Right lateral: right side
touches the cassette
v
Left lateral: left side
touches the cassette
Projections
v Antero-posterior (AP): central ray passes from
anterior to posterior
v
Postero-anterior
(PA): central ray passes from posterior to
anterior
v Lateral: central
ray passes from one side of the body to the other through the axial plane
v Oblique: central ray passes
through the body/body part through a plane which is at an angle to the transverse
plane/coronal plane